Table of Contents
ToggleWhat does LED mean?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. This acronym is derived from the initial letters of each word in the term “light emitting diode.” This modern device is capable of producing visible, infrared, or ultraviolet light. LEDs achieve this by emitting nearly all colors through the combination of three primary color constituents: red, green, and blue lights.
The advent of LEDs has sparked a revolution in the history of lighting. Their attributes including brightness, cooler operation, energy efficiency, and durability have propelled them to surpass conventional incandescent or CFL bulbs. Presently, LED lights are extensively utilized across diverse settings such as residential, commercial, sports facilities, filming studios, and industrial environments. The array of LED products available in the market is vast, encompassing LED light bulbs, floodlights, color-changing RGB lights, spotlights, security lights, indicator lights, and more.
When delving into LED lighting, it’s important to note the two main types: COB (Chip-on-Board) and SMD (Surface Mount Device) LEDs. Each type exhibits subtle variations in its operational characteristics, contributing to their suitability for different applications.
What does LED Stand For?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. Let’s break down each term:
| Terms | Definitions |
| Light | This refers to artificial illumination utilized to render objects visible, usually in the form of visible light. It encompasses the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. |
| Emitting | This denotes the action of discharging photons or light energy. In the context of LEDs, it signifies the process by which light is produced when electrons recombine with electron holes within the semiconductor material. |
| Diode | A diode is an electronic circuit component that permits current flow in one direction while blocking it in the reverse direction. It is typically composed of semiconductor material such as silicon or germanium. In the case of an LED, the semiconductor material undergoes electron excitation when a forward voltage is applied, resulting in the emission of light. |
When a direct current (DC) passes through the LED, typically at around 12 volts, the diode emits bright light as a consequence of electron recombination. By incorporating an LED lens with specific beam angles, it is possible to manipulate the emitted light to create spotlights or floodlights, tailoring the illumination to suit various applications.
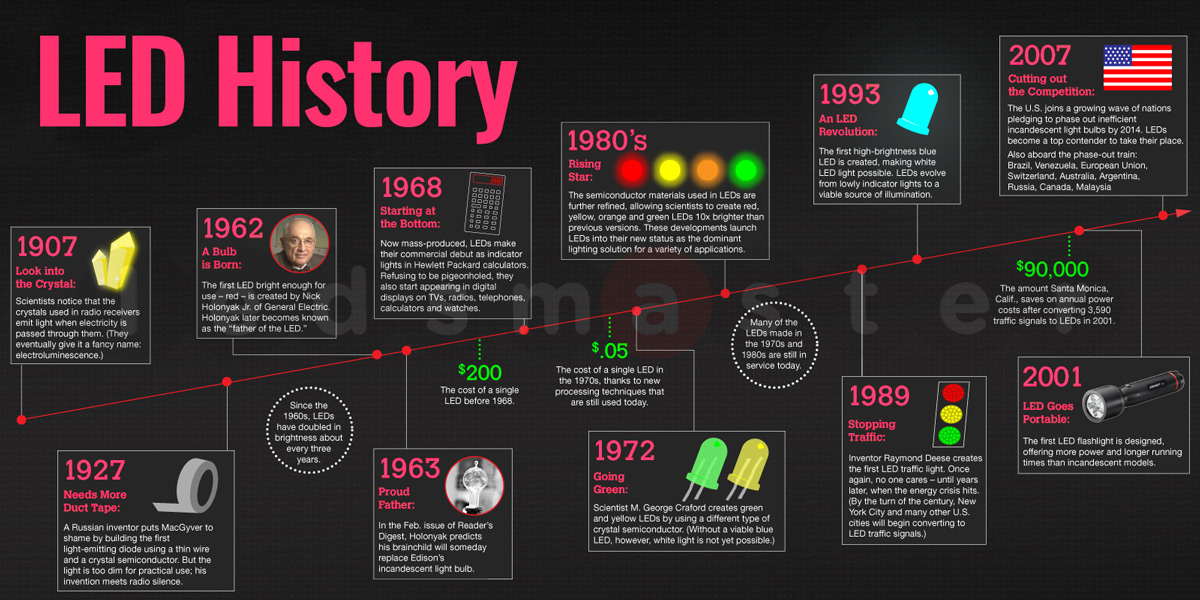
What is the LED Symbol?
The symbol representing a light emitting diode in a circuit diagram is distinctive and comprises several elements. It typically features a triangle, a vertical line, and two arrows. Fundamentally, it resembles the standard diode symbol, but with the inclusion of two extra arrows, signifying the emission of light.
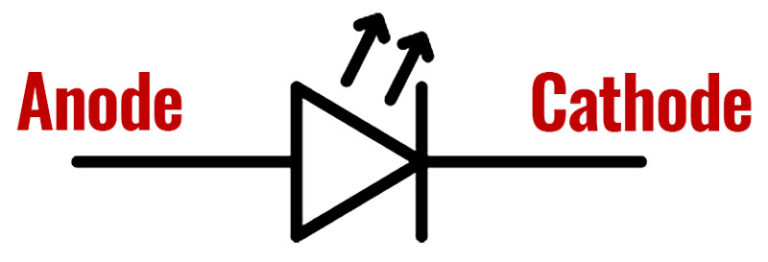
When sketching an LED circuit diagram, it’s imperative to adhere to correct polarity. Ensuring that the positive pole of the battery is connected to the LED’s anode is crucial for proper operation. If this connection is reversed, the LED bulbs will fail to illuminate. In this configuration, the flow of current originates from the battery, travels through the LED, then passes through any associated resistor, before returning to the battery’s negative pole. This unidirectional flow is essential for the LED to function effectively and emit light.
Maintaining polarity is vital not only for LED circuit diagrams but also for practical applications involving LED components. Incorrect polarity can result in damage to the LED and prevent it from operating as intended. Therefore, attention to detail when connecting LEDs in circuits is paramount for achieving desired functionality and avoiding potential issues.
How Does an LED Work?

Understanding the operational mechanism of an LED is pivotal in grasping its functionality, particularly in terms of light production.
At the core of an LED lies the semiconductor, a crucial component responsible for its operation. When an electrical current flows through the circuit, a fascinating interplay occurs within the semiconductor. In the P-type semiconductor, holes exist, while in the N-type semiconductor, electrons abound. As the current traverses the circuit, these electrons and holes join forces, initiating a process where electrons transition from a higher energy state to a lower one. This transition results in the emission of photons, with each photon carrying energy equivalent to the difference in energy levels. Essentially, the valence band (comprising the holes) serves as a platform for electrons to descend to lower energy levels.
| Light Color | LED Semiconductor |
| Red or yellow | Aluminum Gallium Arsenide Phosphide |
| Green | Gallium Nitride |
| Blue | Zinc Selenide |
The choice of P-type and N-type semiconductors plays a crucial role in determining the wavelength of the emitted photons and consequently the color of the light produced. Various semiconductors are employed in LEDs to achieve different light colors. For instance, aluminum gallium arsenide phosphide is utilized for red or yellow light, gallium nitride for green light, and zinc selenide for blue light. Through the strategic combination of these semiconductor materials, LEDs are capable of emitting a wide spectrum of colors, making them versatile and adaptable across numerous applications.
The Evolution of LED Lighting
LED stands as one of humanity’s most significant inventions, providing solutions to numerous issues associated with traditional lighting technologies such as incandescent, metal halide, and CFL lighting. In comparison to incandescent bulbs, which have short lifespans, metal halide lamps requiring extended warm-up times, and CFLs containing toxic mercury, LEDs offer substantial improvements. They boast a lifespan that is 50 to 80 times longer, reach maximum brightness almost instantly, and do not contain hazardous chemicals, making them environmentally friendly upon disposal. Additionally, LEDs exhibit tenfold higher energy efficiency compared to incandescent bulbs, addressing historical energy consumption challenges.
1900s
In the early 20th century, groundbreaking observations laid the foundation for LED technology. Henry Joseph Round, while at Marconi Labs, discovered the emission of yellow light when applying voltage to carborundum crystals. However, it wasn’t until 1927 that Russian scientist Oleg Losev provided an explanation for this phenomenon involving carborundum’s detection and oscillation effects.
1950s
In 1955, Rubin Braunstein’s observation revealed that simple diodes emitted infrared light when subjected to a current. Subsequently, Gary Pittman and Bob Biard, working at Texas Instruments, patented the infrared LED after discovering that gallium arsenide diodes emit infrared light. Despite this breakthrough, their technology initially lacked widespread recognition due to the invisibility of infrared light to the human eye.
1960s and 1970s
The 1960s marked the introduction of the first functional LED lighting by GE scientist Nick Holonyak Jr. This development featured the GaAsP (Gallium Arsenide Phosphide) bulb, the first to utilize semiconductor material in red LED bulbs. M. George Craford, a student of Holonyak’s, pioneered the creation of the first yellow LED by combining red and green gallium phosphide chips. Simultaneously, Thomas P. Pearsall enhanced LED brightness, notably contributing to fiber optics and telecommunications. In Japan, Shuji Nakamura’s research culminated in the development of the first blue LED in 1979, later commercialized in 1994.
Commercialization and Expansion
Initially confined to industrial and laboratory settings due to production costs, LED technology saw a transformative shift with Fairchild Semiconductors’ development of a cost-effective diode manufacturing technique. This innovation drastically reduced LED production costs, making them commercially viable. Consequently, LEDs became prevalent in various commercial and manufacturing applications.
Further advancements, including the invention of white light LEDs through blue chip coating with fluorescent phosphors, were supported by the US Department of Energy. This backing aimed to promote cost-effective LED technology adoption in lighting manufacturing and commercial spaces.
Significance of LED Lights
The advent of LEDs heralded a revolutionary transformation in the lighting industry, offering solutions to longstanding issues associated with traditional lighting sources.
Top 3 Incandescent Bulb Disadvantages
Prior to the widespread adoption of LED bulbs, incandescent lighting was the dominant technology, yet it came with numerous drawbacks. Firstly, incandescent bulbs were highly inefficient, converting only a small fraction of energy into visible light while dissipating the majority as heat. Typically, around 90-95% of the electrical energy used by an incandescent bulb was wasted as heat, leaving only 5-10% to generate light. This inefficiency not only led to higher electricity consumption but also increased energy costs for consumers and businesses alike. Moreover, the excessive heat generated by incandescent bulbs often required additional cooling efforts in illuminated spaces, further compounding energy usage and costs.
Secondly, the high operating temperature of incandescent bulbs presented significant safety hazards. The filament inside these bulbs needed to reach temperatures of around 2000-3000°C to emit light, resulting in an extremely hot surface that could cause burns if touched accidentally. This posed a particular risk in households with children or pets and in workplaces where contact with the bulbs was more likely. Additionally, the heat generated could pose a fire risk if the bulbs were placed too close to flammable materials or used in enclosed fixtures without adequate ventilation. The combination of high surface temperatures and the potential for contact injuries or fires underscored the inherent dangers associated with incandescent lighting.
Lastly, the short lifespan of incandescent bulbs, typically ranging from 1,000 to 2,000 hours, necessitated frequent replacements. This short operational life meant that consumers and businesses faced regular expenditures on new bulbs, adding to overall lighting costs. Frequent bulb replacements also contributed to significant waste, as discarded bulbs often ended up in landfills. The continuous need for new bulbs not only strained financial resources but also led to the consumption of raw materials and increased environmental impact due to the production and disposal processes.
Advantages of LEDs over Incandescent and CFL
In contrast to incandescent bulbs, LEDs have effectively addressed these significant shortcomings through a combination of advanced technology and design. LEDs use semiconductor materials to convert approximately 95% of the electrical energy they consume directly into light, compared to the mere 5-10% efficiency of incandescent bulbs. This remarkable efficiency is achieved through a process called electroluminescence, where electrical current passes through a semiconductor, causing electrons to recombine with holes, thereby releasing energy in the form of photons. Consequently, LEDs require far less power to produce the same amount of light. For instance, a 10W LED bulb can generate brightness equivalent to that of a 100W incandescent bulb, offering a 90% reduction in energy consumption for the same luminous output. This dramatic improvement not only lowers energy bills for consumers and businesses but also contributes significantly to reducing the overall energy demand, thus supporting environmental sustainability and energy conservation efforts.
Furthermore, LEDs operate at much lower temperatures compared to incandescent bulbs, which reduces safety hazards significantly. Incandescent bulbs generate light by heating a tungsten filament to high temperatures, making them hot to the touch and increasing the risk of burns or even fires if they come into contact with flammable materials. In contrast, LEDs produce light through the excitation of electrons within a semiconductor, a process that emits minimal heat. The reduced operating temperature of LEDs not only enhances safety by preventing accidental burns and reducing fire risks but also contributes to their longevity and performance stability. LEDs typically last tens of thousands of hours, far surpassing the lifespan of incandescent and even compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), which further minimizes maintenance costs and the environmental impact associated with frequent replacements.
While CFLs represented a middle ground in terms of energy efficiency and longevity between incandescent and LED bulbs, they came with their own set of environmental concerns, particularly due to their mercury content. Mercury, an essential component in CFLs, allows these bulbs to produce UV light, which is then converted to visible light by a phosphor coating. However, the disposal of CFLs poses a significant environmental risk, as mercury is a potent neurotoxin that can contaminate water bodies and ecosystems if not properly managed. LED technology eliminates these environmental hazards by avoiding the use of mercury and controlling the emitted light wavelengths precisely, thus ensuring no harmful UV radiation is released. This aspect makes LEDs not only a safer choice for both consumers and the environment but also a more responsible lighting solution that aligns with modern sustainability practices.
How to Choose the Best LED Lights?
When selecting the best LED lights, there are several critical factors to consider to ensure they meet your needs. These factors include energy efficiency, lifespan, color temperature, and more. Here’s a detailed guide on what to look for:
Energy and Cost Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of using LED lights is their significant energy and cost savings. LEDs are remarkably efficient, with a high luminous efficacy typically around 130 to 180 lumens per watt (lm/W), which is about ten times more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. This efficiency allows you to reduce energy consumption substantially. For instance, a 10W LED bulb can provide the same brightness as a 100W incandescent bulb, resulting in an approximately 90% reduction in energy use. When shopping for LEDs, look for bulbs with a high luminous efficacy rating. Be cautious of exaggerated claims, such as bulbs purportedly offering 160 or 200 lm/W, as these are often misleading. By choosing energy-efficient LEDs, you can significantly lower your electricity bills and contribute to energy conservation.
Longevity and Durability
LEDs are known for their impressive longevity. Most LED bulbs and floodlights available today offer a lifespan ranging from 60,000 to 120,000 hours. Such extended service life drastically reduces the frequency of replacements, cutting down on both the costs associated with purchasing new bulbs and the labor involved in installations. This durability is especially beneficial for home renovations and large-scale commercial or industrial lighting projects, where long-lasting LEDs minimize maintenance needs and operational disruptions.
Instant Brightness and Color Versatility
Unlike metal halide lamps, which require a warm-up period of 5 to 10 minutes to reach full brightness, LEDs offer instant illumination, turning on and off without delay. This feature is particularly advantageous for outdoor activities, such as backyard gatherings or sports events, where immediate bright lighting is essential. Additionally, LEDs offer versatility in color temperature, typically ranging from 2800K to 3500K for warm white light and 6000K to 7500K for cool white light. Warm white light is ideal for creating a cozy and inviting atmosphere in living rooms and bedrooms, while cool white light is better suited for spaces requiring high visibility, such as sports fields and workspaces. Advanced LED options even allow for bi-color adjustments, enabling users to customize the color temperature according to specific needs and preferences.
High Color Rendering Index (CRI)
The Color Rendering Index (CRI) is a crucial metric for evaluating the quality of light emitted by LEDs. CRI measures how accurately a light source reveals the colors of objects compared to natural sunlight, which has a CRI of 100. LEDs with a CRI of 80 or higher are generally suitable for most residential and commercial applications, providing a realistic representation of colors. For specialized settings like museums or art galleries, where precise color rendering is essential, LEDs with a CRI of 90 or higher are preferred. High-CRI LEDs enhance visual clarity and provide a more vivid and true-to-life lighting experience.
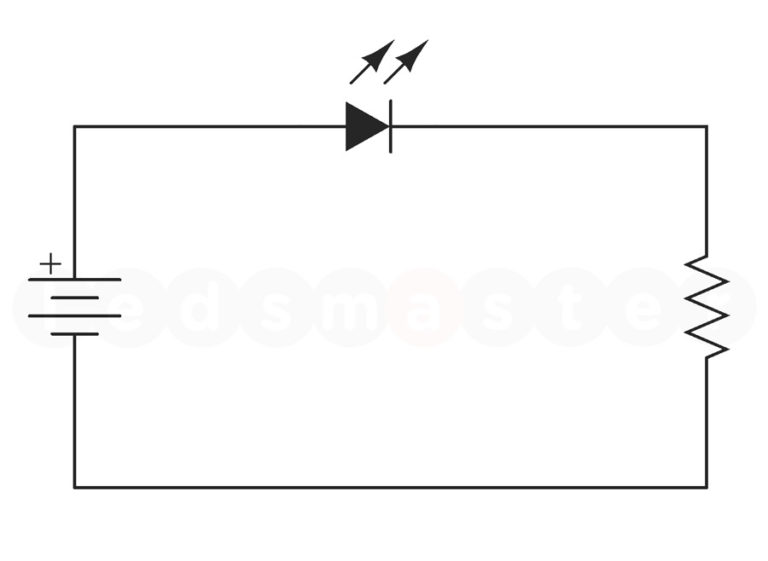
Adjustable Beam Angles
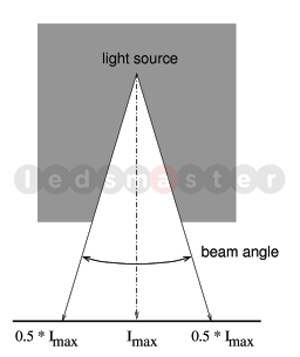 Beam angle is another important factor in choosing the best LED lights, as it determines how light is distributed across a space. Common beam angles include 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, and 120°. A smaller beam angle results in a concentrated light beam, making it ideal for spotlights, whereas a larger beam angle provides broader coverage suitable for floodlights. When planning lighting for an area, such as a backyard, warehouse, or sports field, it’s essential to select LEDs with appropriate beam angles to ensure optimal light distribution and uniformity. Proper beam angle selection enhances visibility and reduces glare, creating a more comfortable and efficient lighting environment.
Beam angle is another important factor in choosing the best LED lights, as it determines how light is distributed across a space. Common beam angles include 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, and 120°. A smaller beam angle results in a concentrated light beam, making it ideal for spotlights, whereas a larger beam angle provides broader coverage suitable for floodlights. When planning lighting for an area, such as a backyard, warehouse, or sports field, it’s essential to select LEDs with appropriate beam angles to ensure optimal light distribution and uniformity. Proper beam angle selection enhances visibility and reduces glare, creating a more comfortable and efficient lighting environment.
Environmental Adaptability
LED lights are also notable for their ability to operate in extreme temperatures, thanks to their robust solid-state design. Unlike traditional lighting technologies that may contain delicate components like filaments, LEDs are resilient and can function in a wide range of environments, from freezing cold to scorching hot. With suitable protective casing and customized optics, LED luminaires can reliably operate in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C, making them ideal for industrial applications and outdoor settings exposed to harsh weather conditions.
LED Luminaires for Extreme Temperatures
In industrial settings and harsh outdoor environments, lighting solutions must endure a broad spectrum of temperatures, from searing heat to bitter cold. LED luminaires are exceptionally well-suited for these conditions because of their solid-state design, which inherently avoids the pitfalls of traditional lighting technologies that rely on fragile components like filaments. Filaments and other delicate parts found in incandescent or CFL bulbs can deteriorate or fail when subjected to significant thermal variations. In contrast, LEDs are more resilient because they use semiconductors, which are stable under a wider range of temperatures.
Customized optics and protective casings enhance the durability and functionality of LED luminaires in extreme environments. These features help in maintaining optimal light output and efficiency even when exposed to challenging conditions. For example, LEDs used in industrial applications are often encased in robust housings that shield the internal components from dust, moisture, and physical impact. This protection is crucial in settings like manufacturing plants, where machinery and processes can create harsh environments, or in cold storage facilities where temperatures plummet well below freezing.
LEDs are designed to function within a broad operational temperature range, typically from -40°C to 100°C. This wide range allows them to perform reliably in diverse applications.
| Applications | Descriptions |
| Manufacturing Plants | LED luminaires can withstand the high heat generated by industrial processes without degrading in performance. |
| Cold Storage | In environments where temperatures are consistently low, such as cold storage warehouses or refrigerated transport, LEDs continue to operate efficiently without the risk of brittle failure or dimming. |
| Outdoor Installations | LEDs are ideal for street lighting, exterior building illumination, and other outdoor uses, where they can handle both the sweltering heat of summer and the frigid conditions of winter. |
Moreover, LEDs do not suffer from the “warm-up” time required by other lighting technologies such as metal halides, which need time to reach their full brightness, especially in cold conditions. LEDs provide instant illumination, which is beneficial in applications where immediate lighting is necessary for safety and efficiency, such as in emergency exit pathways or outdoor security lighting.
LED Dimming and Color-Changing Control
One of the standout features of modern LED lighting is its dimming capability and the ability to change colors. Dimmable LEDs provide flexibility by allowing you to adjust brightness levels to suit various activities. For example, you can dim outdoor floodlights for a relaxed ambiance during a backyard dinner or increase brightness for tasks like lawn mowing. Additionally, many LEDs come with RGB color-changing functions, enabling you to create up to 16 million colors by adjusting the intensity of red, green, and blue components. With wireless DMX controllers, you can conveniently manage these lighting effects from your smartphone or computer, making them perfect for seasonal decorations or creating specific moods.
Compact and Lightweight LED Design
When selecting the best LED lighting, consider the weight and size of the fixtures. A compact and lightweight design ensures safety and reduces installation costs, as heavy luminaires might require additional structural support. Before purchasing, check the weight limitations of your mounting site to ensure compatibility. This helps in choosing a product that fits your specific needs without necessitating expensive reinforcements.
Mitigating Blue Light Pollution
Blue light is a component of visible light with a wavelength ranging from approximately 450 to 495 nanometers. While it is beneficial in regulating our circadian rhythms and maintaining alertness during the day, excessive exposure, especially during the evening, can disrupt sleep patterns. The human eye is particularly sensitive to blue light, which can suppress the production of melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles. This suppression can lead to difficulties in falling asleep and reduced sleep quality, which is why managing blue light exposure from LED lighting is crucial for maintaining healthy sleep patterns.
Impact on Sleep Patterns
Exposure to blue light in the evening can interfere with the body’s natural sleep cycle by inhibiting melatonin production. This interference is particularly problematic because melatonin levels typically rise in the evening to prepare the body for sleep. When blue light exposure from devices or lighting continues into the evening, it can delay the onset of sleep and reduce the overall sleep duration. This effect is more pronounced with LEDs that emit higher levels of blue light, which are commonly used due to their energy efficiency and bright, cool white light.
To mitigate these effects, it is advisable to use LEDs with lower color temperatures in environments where evening use is common. LEDs with color temperatures in the range of 2800K to 3500K produce a warm, yellowish-orange light that is less likely to disrupt melatonin production. This spectrum is closer to the natural light at sunrise or sunset, which helps the body transition more smoothly into a restful state. By creating a lighting environment that mimics natural light cycles, you can help maintain your body’s biological rhythms and improve sleep quality.
Creating a Cozy and Relaxing Atmosphere
Lower color temperature LEDs not only reduce blue light exposure but also enhance the ambiance of indoor and outdoor spaces. Warm-colored LEDs are particularly effective in creating a cozy and inviting atmosphere, which is ideal for relaxation and social activities in living rooms, bedrooms, and gardens. The softer, more diffused light reduces glare and creates a comfortable environment that is conducive to unwinding after a long day. This is especially beneficial in areas where mood lighting is desired, such as in dining rooms or patio areas, where a warm and inviting light can enhance the overall experience.
For example, in bedrooms, using warm white LEDs for bedside lamps or ceiling fixtures can create a soothing environment that promotes relaxation and prepares the mind and body for sleep. In gardens or patio areas, warm LED string lights or path lights can transform the space into a relaxing retreat, ideal for evening gatherings or quiet reflection. This approach not only improves the visual comfort of the space but also aligns with circadian-friendly lighting practices that support better sleep health.
Evaluating the Price of LED Lights
LED lights are renowned for their energy efficiency, durability, and longevity, but they often come with a higher upfront cost compared to traditional lighting options such as incandescent or HID bulbs. However, this initial investment is offset by the significant long-term savings that LEDs offer. By considering the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price, it becomes evident that LEDs are a wise investment that can yield substantial financial benefits over their extended lifespan.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
One of the most significant advantages of LED lighting is its extended lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements. Unlike traditional lighting options like halogen floodlights, which may require frequent replacements due to lumen depreciation or filament failure, LEDs can last between 10 to 30 years under normal usage conditions. This longevity translates to reduced maintenance costs over the lifespan of the LED fixture. By investing in LEDs, businesses and homeowners can avoid the expense and inconvenience associated with frequent bulb replacements and maintenance visits, leading to substantial savings in the long run.
Extended Lifespan
LEDs are known for their exceptional durability and resilience to shock, vibration, and temperature fluctuations. Unlike traditional bulbs that contain fragile filaments or glass envelopes, LEDs utilize solid-state components that are less susceptible to physical damage. This inherent robustness contributes to their longevity and reliability, ensuring consistent performance over an extended period. With an average lifespan of up to 30 years, LEDs outlast conventional lighting options by a significant margin, resulting in long-term cost savings for both residential and commercial users.
Conclusion
The transition to LED lighting offers numerous benefits, including extended lifespan, minimal maintenance requirements, substantial energy savings, and environmental conservation. Despite the higher initial cost, the long-term advantages of LEDs make them a cost-effective and sustainable lighting solution for residential and commercial applications. By prioritizing efficiency, durability, and financial savings, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions that enhance both their lighting quality and their bottom line over time.