LED vs HPS – Comparison and Replacement Guide

LED and HPS are the mainstream lighting devices for large areas. They can be applied to sports field lighting, street light, airport, warehouse, backyard, high mast, high bay flood lights and so on. In the past, many site owners were prone to HPS or LPS flood lights because of its low price and availability; however, LED replacement becomes a new option for large area lighting. This passage provides a guideline for you to do the comparison between HPS and LED. You are always welcome to contact us for HPS LED replacement of 100W, 200W, 300W, 400W, 500W, 1000W, 2000W, 3000W, 4000W, 5000W lighting.
Advantage of LED over HPS Lights
1. The LED light beam is concentrated, and thus there is less wastage of energy due to light diffusion. However, the HPS flood lamps emit light in all direction, and thus the lighting efficiency is externally reduced.
2. LED is a new generation of lighting that gives higher luminous efficiency (130 to 150 lm/W) than HPS (50 to 100 lm/W). LED has higher energy efficiency.
3. The color rendering index (CRI) of the LED lamp is higher than that of the high-pressure sodium lamp. The CRI of common high pressure sodium lamp is around 20 to 30, whereas that for LED street light or flood light reach 80. High CRI of LED is important for safety because the human eye is more sensitive in the environment lighted up by high CRI lighting. The road users can have lower reaction time to identify the dangerous situations.
4. The lumen depreciation (decrease in brightness) of LED light is very low, which is less than 3% per year. The LED works at least 10 years to have 30% lumen decrease that is noticeable by naked eyes.
5. LED light is dimmable but HPS does not. Dimming is especially important for audiences as gradual increase or decrease of brightness is less irritating to eyes.
6. LED is operated under low-voltage DC, which is safer to use 12V or 24V. With its low power consumption, LED light is compatible to majority of renewable energy system such as solar power panel and wind power turbine.
7. HPS has lifespan of around 20000 to 30000 hours, while LED has 80000 hours. You have need to maintenance the LED lighting after doing the HPS-LED replacement.
8. LED can be switched on and off vigorously without damaging them. However, it is not applicable to HPS as it needs warm up time and frequent turning on and off will decrease their service life.
9. LED supports IP66 because it used a completely different structural and electronic design, which is seldom found in HPS luminary.
10. Excellent heat dissipation of LED. The junction temperature of LED chip is lower than 70C after running for hours, which is 30 to 40% less than HPS lamps.
11. Our brand-new LED light series have overheat protection module. If the monitoring unit detects abnormally high temperature, the flood lights will be temporarily shut down to protect the entire structure. This feature is optional and free to add or remove.
12. LED luminary does not contain harmful material such as mercury, halogen as found in the HPS. LED is a better, more environmentally friendly light source for all areas.

What is High Pressure Sodium (HPS)?
High-pressure sodium lamp emits golden or warm light. HPS were developed in the 1960s and having the alternative name of “third-generation” light source. They are high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps that contain the tungsten electrode. Unlike the low-pressure sodium lamp, the high-pressure sodium lamp is no longer a monochromatic yellow light but spreads over a relatively wide frequency range. Since the high-pressure sodium lamp has the advantages of high luminous efficacy, long lifespan, acceptable color rendering properties, no attracting of insects, and low fading color for the photographed object, the high pressure sodium lamp (HPS) is widely used in all corners of general lighting, and to gradually replace high pressure mercury lamp. The recently developed color-improving and high-coloration high-pressure sodium lamps can replace incandescent lamps and achieve great energy-saving effects.
How It Works – Mechanism of HPS
The initial stage is the low-pressure discharge of mercury vapor and helium. At this time, the working voltage of the bulb is very low and the current is very large; as the discharge process continues, the temperature of the arc gradually rises, and the vapor pressure of mercury and sodium is determined by the temperature of the coldest end of the discharge tube. When the temperature of the cold junction of the discharge tube reaches a stable level, the discharge tends to be stable, and the luminous flux, operating voltage, operating current, and power of the bulb are also in normal operation. Under normal operating conditions, the entire start up process takes about 10 minutes.

The fluctuation of the power supply voltage will cause changes in the electrical parameters of the lamp. If the supply voltage rises, the operating current of the lamp will increase. The temperature of vapor pressure of mercury and sodium increases with the cold junction of the arc tube, and then, the operating voltage and lamp power will increase accordingly. As a result, the life of the lamp is greatly reduced; conversely, if the power supply voltage is reduced, the light does not work properly, the luminous efficiency is lowered, and the lamp may not be started by itself. Therefore, it is required that when the lamp is used, the fluctuation of the power supply voltage should not be too large, and it is generally required to change within 5% of the rated value.
When the lamp starts, an electric arc is generated between the electrodes at both ends of the arc tube. Due to the high temperature of the arc, the liquid sodium mercury vapor in the tube evaporates into mercury vapor and sodium vapor, and the electrons emitted from the cathode collide with the discharge material during the movement to the anode. The atoms of an atom are made to ionize or excite energy, and then return from the excited state to the ground state; or from the ionized state to the excited state, and then return to the base state in an infinite cycle. At this time, the excess energy is released in the form of light radiation. Generated light. The vapor pressure of the discharge material in the high pressure sodium lamp is very high, that is, the density of sodium atoms is high, and the number of collisions between the electron and the sodium atom is frequent, so that the resonance radiation spectrum is broadened and other visible spectrum radiation occurs, so the light color of the high pressure sodium lamp is superior low pressure sodium lamp. The high-pressure sodium lamp is a high-intensity gas discharge lamp. Due to the negative resistance of the gas discharge lamp, if the lamp is connected to the power grid alone, its working state is unstable. As the discharge process continues, it will cause the current in the circuit to increase indefinitely, and finally it will reach the lamp or circuit. The parts were burned.
LED
Light emitting diodes (LED) is made of compounds containing Ga, As, P, N, etc. When electrons and holes recombine, they emit visible light. It can be used as a light, composition of text or digital display. The gallium arsenide diode emits red light, the gallium phosphide diode emits green light, the silicon carbide diode emits yellow light, and the gallium nitride diode emits blue light. Due to chemical properties, organic light emitting diodes and inorganic light emitting diodes are defined as two different categories under LED lighting.
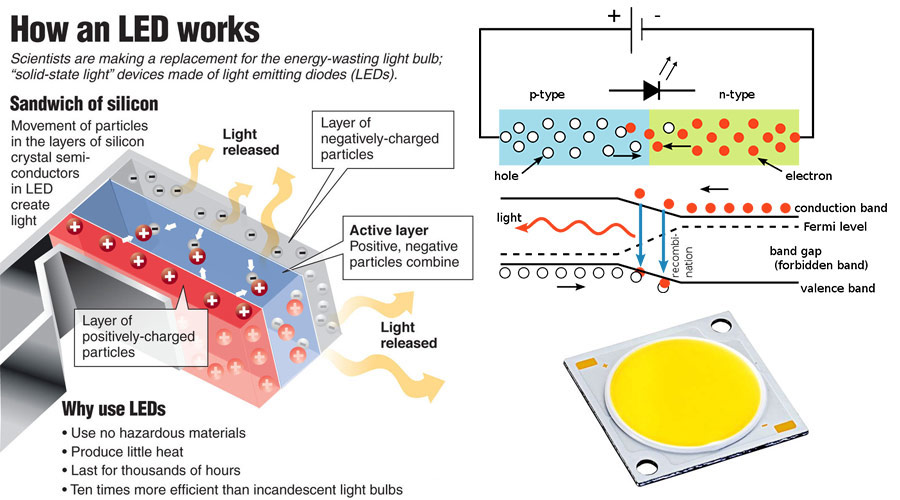
Working Principle of LED Lights
Different semiconductor materials have different energy states for electrons and holes. When the electrons and holes recombine, the difference in energy gap will produce different colors. The more energy is released, the shorter the wavelength of the emitted light. We can see when comparing with HPS, LED uses the current to drive the electron inside the semiconductor, generally without significant heating or warming up process as found in the HPS flood lights.
Invention of White LED
In 1993, Shuji Naka, who was an employee at Nichia Corporation in Japan, invented a semiconductor based on a wide band-gap semiconductor material – gallium nitride (GaN) and indium gallium nitride (InGaN). Blue LED was made with this technology, and this LED has been widely used in the late 1990s. In theory, blue LEDs combined with existing red and green LEDs to produce white light, but white LEDs are rarely created in this way.
Most of the white LEDs currently produced are made by coating a thin-yellow phosphorus layer on a blue LED. When the LED chip emits blue light, part of the blue light is converted to a predominantly yellow light with a broad spectrum of approximately 575 nm in the center of the spectrum. Since yellow light stimulates the red and green light receptors in the naked eye, the blue light of the LED itself is mixed to make it look like white light. This method of producing white LEDs was developed by Nichia Corporation and was used since 1996. Now there are quite a lot of white light LED Technologies, but mostly are based on Nichia’s theory.